Overview
The article underscores the critical importance of augmented reality (AR) jobs and their transformative impact across various industries. It highlights essential roles such as:
- Developers
- Designers
- Project managers
These roles are pivotal for driving innovation and enhancing user engagement in sectors like retail, education, and healthcare. Research indicates a substantial growth in demand for these roles as AR technology continues to evolve, making it imperative for organizations to recognize the value of AR professionals in their strategic planning. By embracing AR, companies can not only stay ahead of the curve but also significantly improve their operational efficiency and customer experience.
Introduction
Augmented reality is rapidly reshaping the landscape of various industries, creating a surge in demand for specialized roles that drive this innovation. As businesses recognize the potential of AR to enhance user engagement and streamline operations, understanding the diverse job opportunities within this field becomes essential.
However, as the industry evolves, what skills and qualifications will be necessary for professionals to thrive in this dynamic environment? This article delves into the significance of augmented reality jobs, exploring key roles, essential skills, and the profound impact AR has on sectors such as retail, education, and healthcare.
Define Augmented Reality Jobs and Their Importance
Augmented reality jobs encompass a variety of roles focused on the creation, development, and implementation of AR technologies and applications. These roles—AR developers, designers, project managers, and content creators—play crucial parts in integrating digital elements into the real world.
The significance of augmented reality jobs lies in their ability to boost user engagement, enhance customer interactions, and drive innovation across multiple sectors, including retail, education, and healthcare. Notably, firms such as an award-winning XR studio are leading this transformation, pioneering immersive AR solutions that significantly elevate brand engagement and customer loyalty.
As AR technology continues to evolve, the demand for augmented reality jobs is projected to grow substantially, making this field an essential area for career development. Now is the time for brand managers to recognize the potential of AR and invest in talent that can harness this technology to propel their organizations forward.
Explore Key Roles in Augmented Reality Development
Explore Key Roles in Augmented Reality Development
Key roles in augmented reality development encompass a range of responsibilities that are essential for the successful implementation of AR technologies.
-
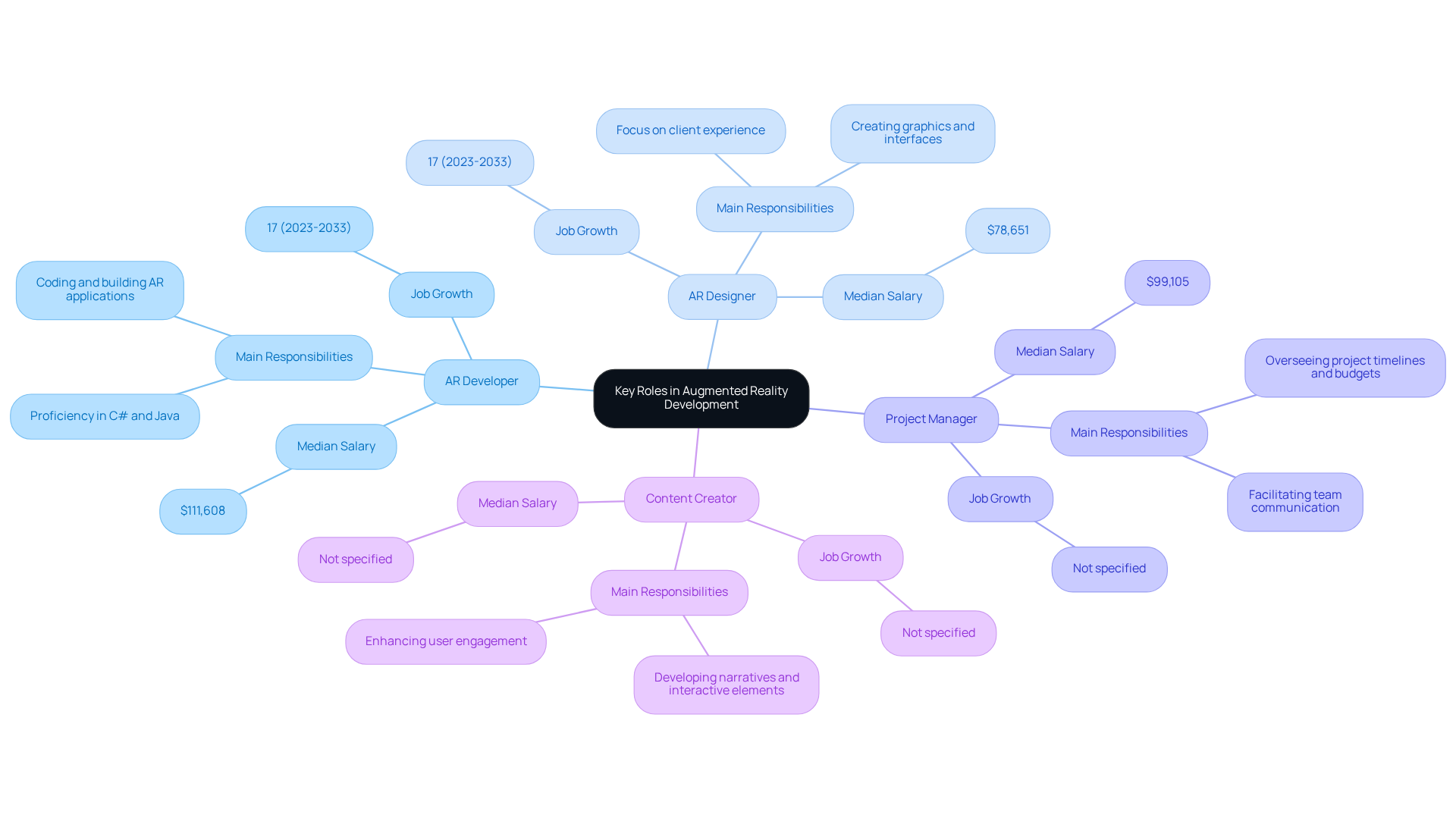
AR Developer: Tasked with coding and building AR applications, AR developers typically require proficiency in programming languages such as C# and Java. Their role is essential in ensuring that the technical aspects of AR interactions function seamlessly. Companies like Magic Playbox leverage skilled AR developers to create innovative solutions that enhance brand engagement. The median annual salary for AR developers in the US is $111,608, with a projected job growth of 17% from 2023 to 2033.
-
AR Designer: Concentrating on the visual aspects of AR interactions, AR designers produce captivating graphics and interfaces that engage individuals. Their expertise in design principles and client experience is vital for crafting immersive environments. The designers of the playbox contribute significantly to creating visually impressive AR applications that connect with consumers. AR designers earn a median annual salary of $78,651, with similar job growth projections of 17%.
-
Project Manager: Overseeing AR projects from conception to completion, project managers ensure that timelines and budgets are adhered to while facilitating communication between various teams. Their organizational skills and ability to manage resources effectively are crucial for project success. The median annual salary for AR project managers is $99,105, reflecting the importance of leadership in AR initiatives.
-
Content Creator: Responsible for developing narratives and interactive elements that enhance user engagement, content creators often come from backgrounds in storytelling and multimedia production. Their creativity plays a significant role in making AR interactions memorable and impactful, as seen in the projects undertaken by Magic Playbox.
Each of these roles highlights the necessity for teamwork and interdisciplinary abilities, as the combination of technology, design, and storytelling is crucial for crafting engaging augmented reality interactions. With the AR market projected to reach $340 billion by 2024, the demand for augmented reality jobs is expected to grow significantly. Furthermore, 63% of individuals express concerns about data security and surveillance associated with AR, emphasizing the necessity of addressing these issues in the advancement of AR technologies. Additionally, 45% of consumers show interest in sustainable AR solutions, indicating an evolving responsibility for AR professionals to consider environmental impacts in their work.
Identify Essential Skills and Qualifications for AR Professionals
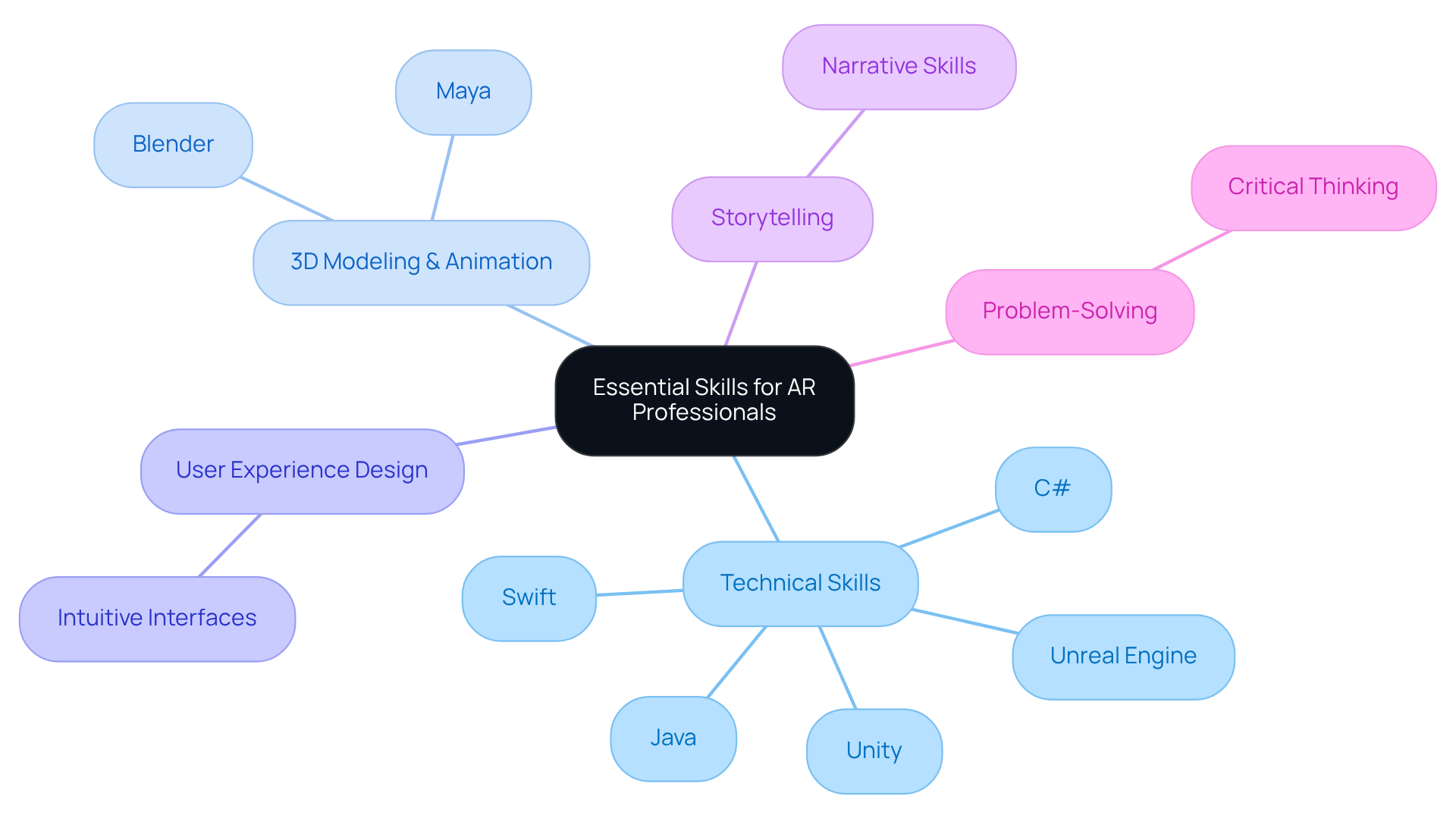
Essential skills and qualifications for AR professionals in 2025 encompass a diverse range of technical and creative competencies, particularly relevant to companies like Magic Playbox that are pioneering immersive AR experiences.
Technical Skills: Proficiency in programming languages such as C#, Java, and Swift is crucial, alongside familiarity with AR development platforms like Unity and Unreal Engine. These skills are foundational for creating robust AR applications that enhance brand engagement.
3D Modeling and Animation: A solid understanding of 3D design tools, including Blender and Maya, is necessary for crafting realistic AR content that engages individuals and supports marketing initiatives.
User Experience (UX) Design: The capability to create intuitive interfaces is essential for improving interaction with AR applications, ensuring a smooth process that encourages client loyalty.
Storytelling: Strong narrative skills are essential for creating engaging content that resonates with users, making the AR interaction more immersive and impactful for brands.
Problem-Solving: Critical thinking abilities are essential for troubleshooting and enhancing AR interactions, enabling professionals to tackle challenges efficiently and innovate within the industry.
Typically, a degree in computer science, graphic design, or a related field is preferred, complemented by a portfolio that showcases relevant projects. As the AR industry evolves, professionals equipped with these skills will be well-positioned to meet the growing demand for innovative AR solutions. Notably, augmented reality modules can boost sales by up to 80%, underscoring the impact of these skills on business outcomes. Tim Cook has forecasted that AR interactions will become as routine as consuming three meals daily, emphasizing the growing importance of AR specialists in the current market. Furthermore, the average annual salary for an AR specialist in India in 2025 is projected to be INR 5L, providing insight into the career prospects within this dynamic field.
Examine the Impact of Augmented Reality on Various Industries
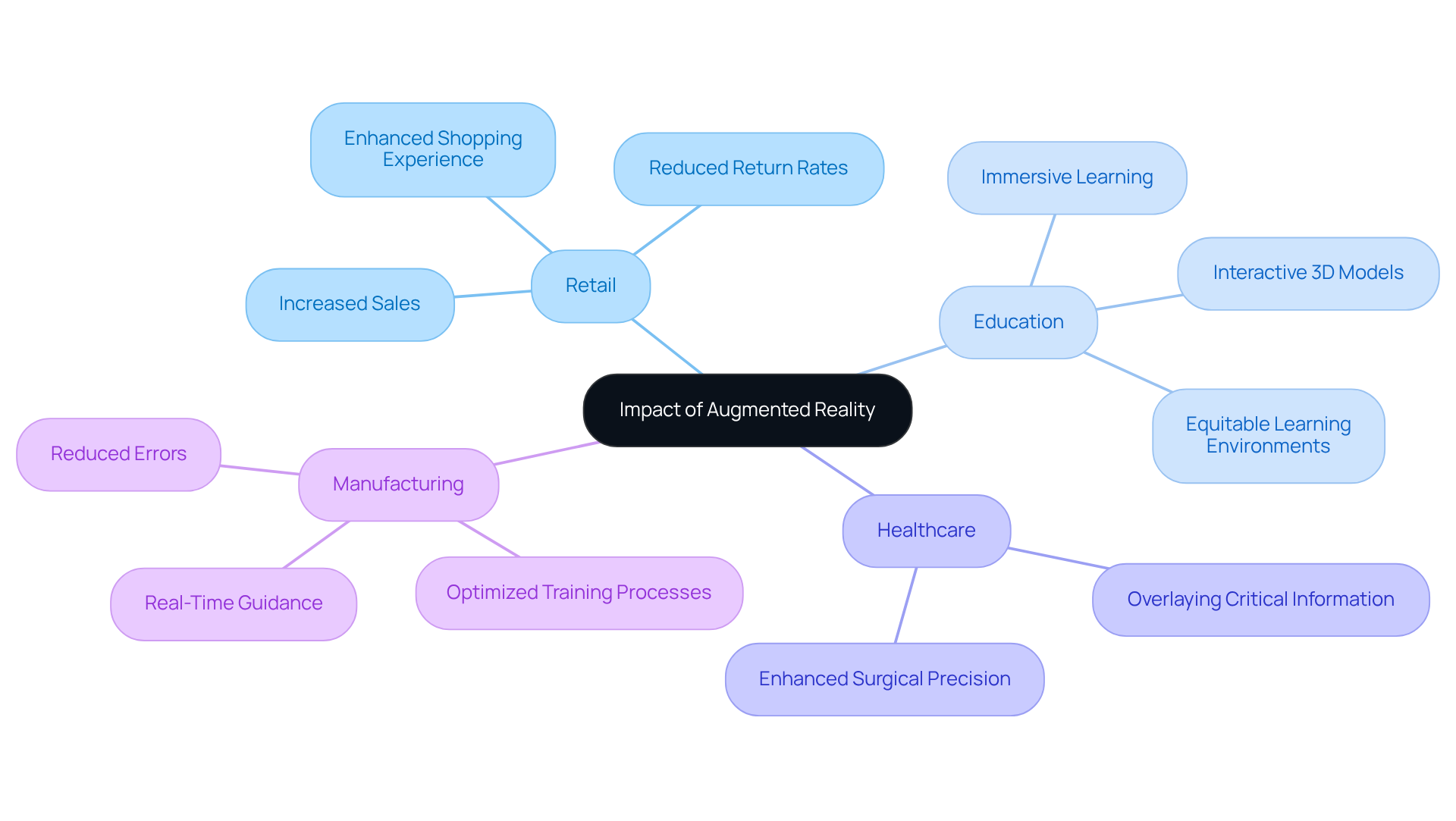
Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing various sectors, with notable advancements in retail and education, particularly through the innovative solutions offered by the company.
- Retail: AR significantly enhances the shopping experience by enabling customers to visualize products within their own environments. This capability not only boosts engagement but also leads to reduced return rates, as consumers can make more informed purchasing decisions. Research indicates that the augmented reality solutions from the company have been shown to increase sales by as much as 80%, underscoring its transformative impact on retail dynamics.
- Education: In the educational sector, AR is facilitating immersive learning experiences that allow students to interact with 3D models and simulations. This hands-on approach enhances retention and comprehension of complex concepts, making learning more engaging. Initiatives like Wonder Kids exemplify how Wonder Box improves educational outcomes by making learning both entertaining and interactive. Furthermore, immersive technologies are being employed to create equitable learning environments, particularly for students with learning disabilities, thus broadening educational opportunities.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, AR is supporting surgical procedures by overlaying critical information directly onto the patient's body, which enhances precision and improves surgical outcomes.
- Manufacturing: AR is optimizing training and maintenance processes in manufacturing by providing real-time guidance and visual instructions. This reduces errors and boosts operational efficiency.
The adoption of AR technology is poised to continue its upward trajectory, with projections indicating a substantial increase in job opportunities and industry investment. As AR becomes more integrated into daily life, its role in enhancing customer engagement and educational experiences will only expand, particularly through the pioneering efforts of Magic Playbox. Collaborating with leaders in the field will be essential to harnessing the full potential of this transformative technology.
Conclusion
The exploration of augmented reality jobs unveils a dynamic and rapidly evolving field poised to shape the future of various industries. As organizations increasingly recognize the potential of AR technologies, the demand for skilled professionals—developers, designers, project managers, and content creators—continues to surge. These roles are crucial not only for the development of innovative applications but also for enhancing user engagement and driving business success across sectors such as retail, education, and healthcare.
Key insights throughout this discussion illuminate:
- The diverse responsibilities associated with augmented reality roles
- The essential skills required for success
- The transformative impact of AR on industries
With a projected market growth to $340 billion by 2024, professionals equipped with technical expertise, creativity, and problem-solving abilities will be integral to meeting the evolving demands of this sector. Furthermore, the emphasis on addressing data security concerns and sustainable practices highlights the multifaceted responsibilities that AR professionals must navigate.
The significance of augmented reality transcends mere job creation; it signifies a pivotal shift in how businesses engage with customers and how educational experiences are delivered. As AR technology becomes increasingly commonplace, opportunities for innovation and collaboration will expand, inviting professionals to engage with this transformative medium. Embracing the potential of augmented reality promises not only to enhance user experiences but also positions organizations to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are augmented reality jobs?
Augmented reality jobs encompass various roles focused on the creation, development, and implementation of AR technologies and applications, including AR developers, designers, project managers, and content creators.
Why are augmented reality jobs important?
Augmented reality jobs are important because they enhance user engagement, improve customer interactions, and drive innovation across multiple sectors such as retail, education, and healthcare.
How do augmented reality jobs impact businesses?
These jobs help integrate digital elements into the real world, significantly elevating brand engagement and customer loyalty, which can lead to improved business performance.
What is the future outlook for augmented reality jobs?
The demand for augmented reality jobs is projected to grow substantially as AR technology continues to evolve, making it a key area for career development.
What should brand managers consider regarding augmented reality?
Brand managers should recognize the potential of AR and invest in talent that can leverage this technology to advance their organizations.




